- Authors: Tayebeh Yousefi, Mansour Taghadosi, Alireza Dabbaghian, Ryan Siu, Gerd Grau, Georg Zoidl, Hossein Kassiri
- Publication date: 2020/9/25
- Journal: IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems
- Volume: 14
- Issue: 6
- Pages: 1274-1286
- Publisher: IEEE
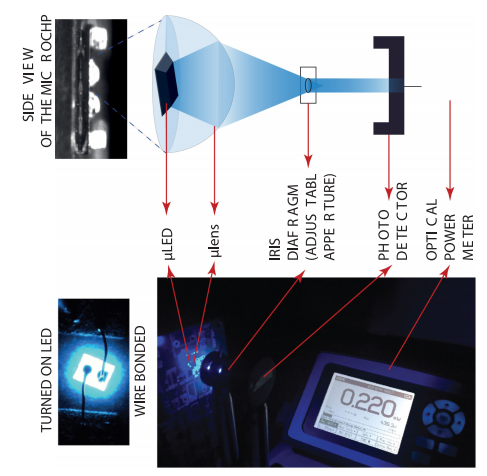
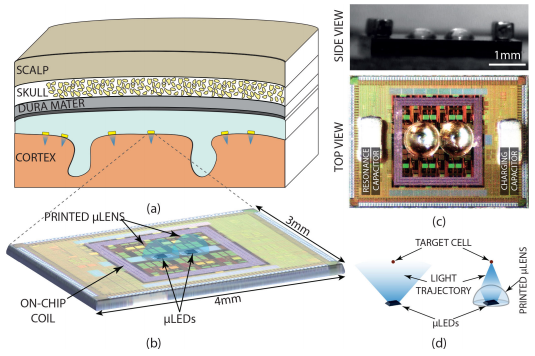
- Abstract: This paper presents an energy-efficient mm-scale self-contained bidirectional optogenetic neuro-stimulator, which employs a novel highly-linear μ LED driving circuit architecture as well as inkjet-printed custom-designed optical μ lenses for light directivity enhancement. The proposed current-mode μ LED driver performs linear control of optical stimulation for the entire target range ( < 10 mA) while requiring the smallest reported headroom, yielding a significant boost in the energy conversion efficiency. A 30.46× improvement in the power delivery efficiency to the target tissue is achieved by employing a pair of printed optical μ lenses. The fabricated SoC also integrates two recording channels for LFP recording and digitization, as well as power management blocks. A micro-coil is also embedded on the chip to receive inductive power and our experimental results show a PTE of 2.24 % for the wireless link. The self-contained system including the μ LEDs, μ lenses and the capacitors required by the power management blocks is sized 6 mm 3 and weighs 12.5 mg. Full experimental measurement results for electrical and optical circuitry as well as in vitro measurement results are reported.